 Well-known PCB supplier
Well-known PCB supplier
+86 13603063656
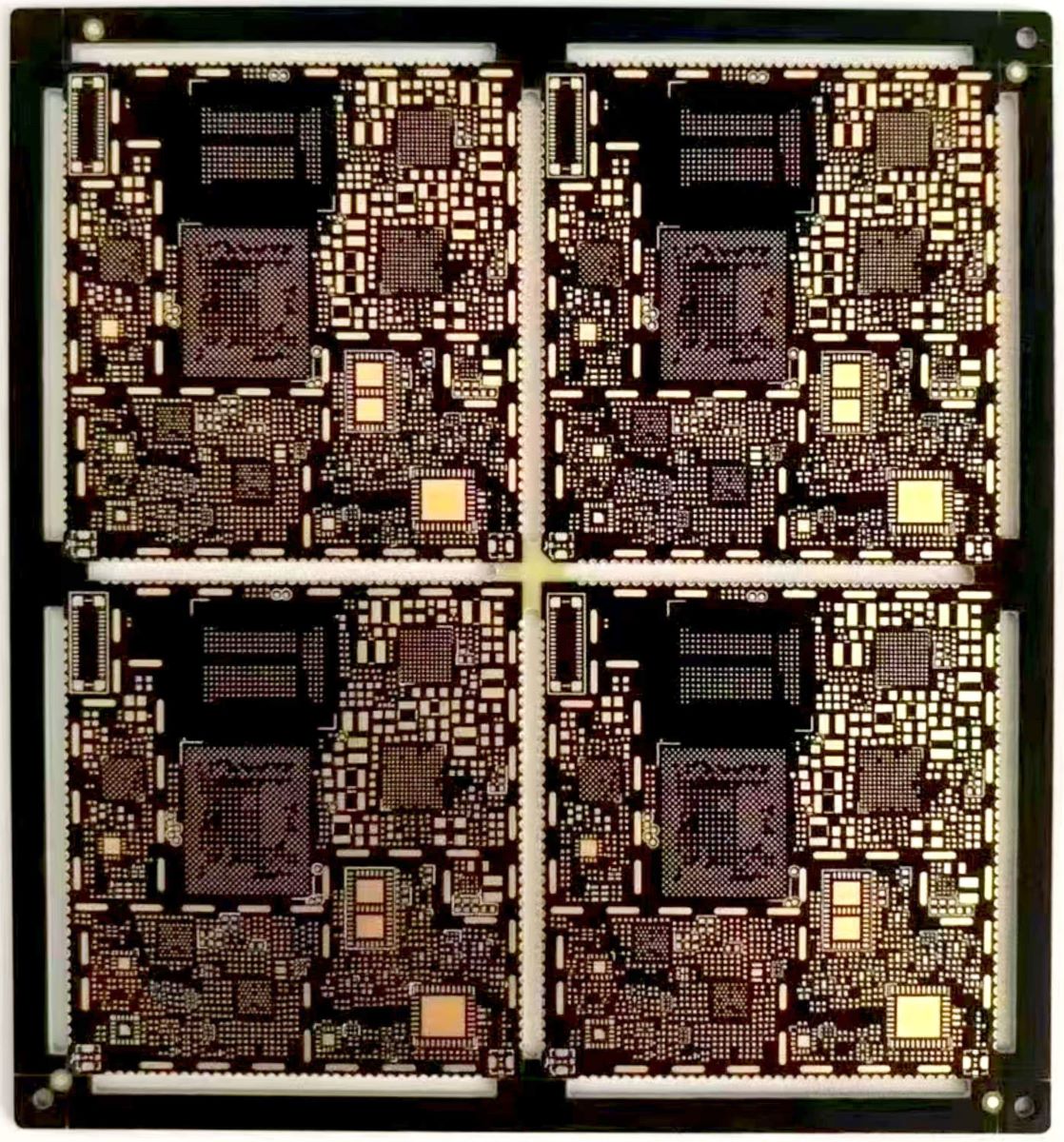
PCB Via Filling, In the PCB industry, via filling is not just a manufacturing step—it is a critical technology that determines the quality, performance, and reliability of a circuit board. Whether for high-speed signal transmission, thermal dissipation optimization, or multilayer board stability, via filling plays a vital role. However, engineers and procurement teams often struggle with several key questions when selecting a via filling method:
This guide will dive deep into different via filling technologies and help you make the best decision for your PCB projects.
PCB Via Filling
In PCB design, vias connect different circuit layers, and via filling refers to completely sealing these vias with filling materials to improve the board’s performance and durability. Depending on the application, filling materials can be resin, copper, epoxy, or solder mask, and different filling methods impact PCB functionality in distinct ways.
Many people confuse via filling with via plugging, but they are fundamentally different:
Understanding this distinction helps engineers avoid unnecessary design mistakes.
Via filling is widely used in high-end electronics, particularly in the following applications:
Different applications require different via filling methods, making the right selection crucial.
✅ Lowest cost
✅ Works for low-end consumer electronics
❌ Not suitable for BGA or high-density designs
✅ Sufficient for most PCB applications
✅ Industry-standard for automotive and motherboard PCBs
✅ Lower cost compared to resin-filled vias
❌ Lower mechanical strength than resin filling
✅ Best mechanical strength
✅ Ideal for high-density interconnects and microvia filling
❌ Higher cost
📌 Cost Comparison (Based on Double-Layer & Four-Layer PCBs):
| PCB Layer Count | Solder Mask Over Via | Ink Plugging | Resin Filling |
|---|---|---|---|
| Double-layer PCB | 1.00 | 1.02 | 2.00 |
| Four-layer PCB | 1.00 | 1.01 | 1.60 |
📢 In most cases, ink plugging is sufficient, especially for automotive electronics and mainstream motherboards, as it balances performance and cost effectively.
✅ Improves electrical performance
✅ Ideal for high-frequency applications
❌ Higher cost and complex manufacturing process
✅ Superior electrical performance
✅ Excellent heat dissipation
❌ High manufacturing cost
🔴 Uneven filling → May cause short circuits or electrical failures.
🔴 Filling material expansion → Affects soldering reliability.
🔴 Trapped air pockets → Can interfere with signal integrity.
✔️ Select high-quality filling materials with good fluidity and adhesion.
✔️ Use vacuum filling processes to eliminate air pockets.
✔️ Perform strict AOI inspections to ensure via quality.
Also IPC has the quality std in thid field
Selecting the right via-filling method depends on your PCB’s application, signal requirements, thermal demands, and budget.
The right choice enhances PCB performance while optimizing manufacturing costs, ensuring long-term reliability in electronic products.
also anything you can communicated with your PCB supplier, they will rpely you the best choice
Connect to a Jerico Multilayer PCB engineer to support your project!
Request A Quote